Windows, oh Windows! It may look like a friendly playground for beginners, but let me tell you, it’s a true powerhouse under the hood, and today, we’re diving into its secret weapons that every developer should know about!
-
Introducing WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux): Ever dreamed of having the best of both worlds? With WSL, you can seamlessly run a full-fledged Linux environment right inside your Windows system. It’s like magic! Developers, this gem will revolutionize your workflow, and I’ll guide you through the wonders it brings in my latest blog post on WSL.
-
PowerShell: A Powerful Tool for Windows System Management Get ready to unleash the ultimate developer tool – Power Shell Scripting! If you’ve ever felt the power of command-line tools, this will take it to a whole new level. But fear not, I’ve got you covered! In this blog post, I’ll walk you through what Power Shell Scripting is, how to use it like a pro, and the reasons why it’s an absolute game-changer for developers.
But wait, there’s more! I won’t just leave you with theory; we’ll dive into some basic commands that will elevate your scripting skills from day one. From automating repetitive tasks to streamlining your workflows, Power Shell will be your new best friend.
And the cherry on top? I’ve got some exciting project ideas that you can embark on using Power Shell Scripting. Trust me; you’ll be amazed at what you can achieve with this incredible tool in your arsenal.
So whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting your coding journey, join me in this adventure, and let’s unlock the full potential of Windows together! Get ready to take your skills to new heights and make your development life a breeze with the power of WSL and Power Shell Scripting.
PowerShell: A Powerful Tool for Windows System Management
PowerShell is a versatile command-line shell and scripting language developed by Microsoft. It is designed to assist IT professionals and system administrators in automating administrative tasks and managing configurations in Windows environments. PowerShell provides access to various system administration objects and APIs, enabling users to interact with and manipulate system components such as the file system, registry, services, processes, and more.
Key Features of PowerShell
-
Object-Oriented: PowerShell treats data as objects rather than plain text, allowing easy manipulation and filtering of output using various cmdlets (commands).
-
Cmdlets: PowerShell cmdlets are small, single-function commands that perform specific tasks. They follow a Verb-Noun naming convention (e.g., Get-Process, Set-Item, New-Service), making it easier to understand their functions.
-
Pipelining: PowerShell allows you to chain commands together using pipes (|), passing the output of one cmdlet as the input to another. This enables users to perform complex operations by combining simple cmdlets.
-
Scripting Language: PowerShell is a full-fledged scripting language with features like variables, loops, conditional statements, functions, and error handling. This makes it ideal for writing automation scripts and managing repetitive tasks.
-
Integration with .NET: PowerShell leverages the .NET Framework, enabling users to access a wide range of .NET classes and assemblies for more advanced scripting capabilities.
-
Remoting: PowerShell supports remote administration, allowing users to execute commands on remote computers in the network.
-
Desired State Configuration (DSC): PowerShell DSC enables administrators to define the desired state of a system or application and ensure that the configurations remain consistent.
PowerShell is not limited to Windows environments. It is also available for cross-platform use, being open-source and available for macOS and various Linux distributions as PowerShell Core. With its rich set of features and capabilities, PowerShell has become an essential tool in the IT world for automation, administration, and management of Windows environments.
Basic PowerShell Commands
PowerShell offers a wide range of commands to navigate and manage your system efficiently. Here are some essential basic commands to help you get started:
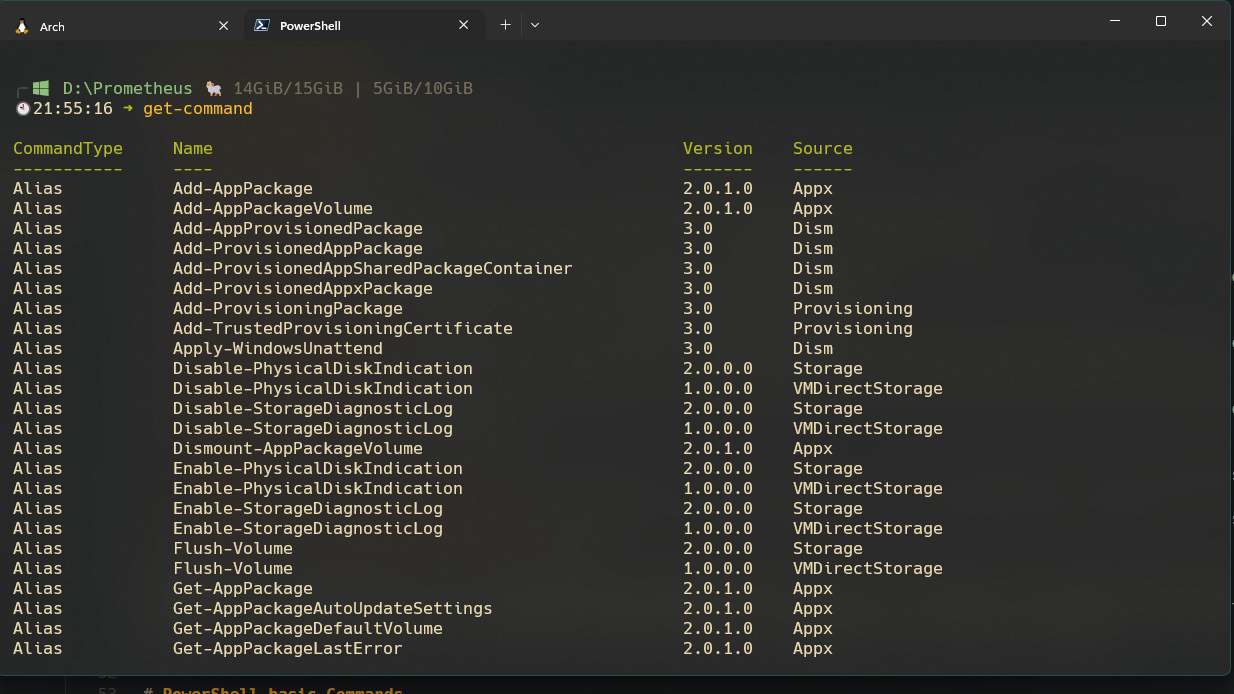
Get-Command
The Get-Command cmdlet provides an easy-to-use reference of all available commands in your current session. Simply type this command in the PowerShell terminal to view the comprehensive list of commands at your disposal.
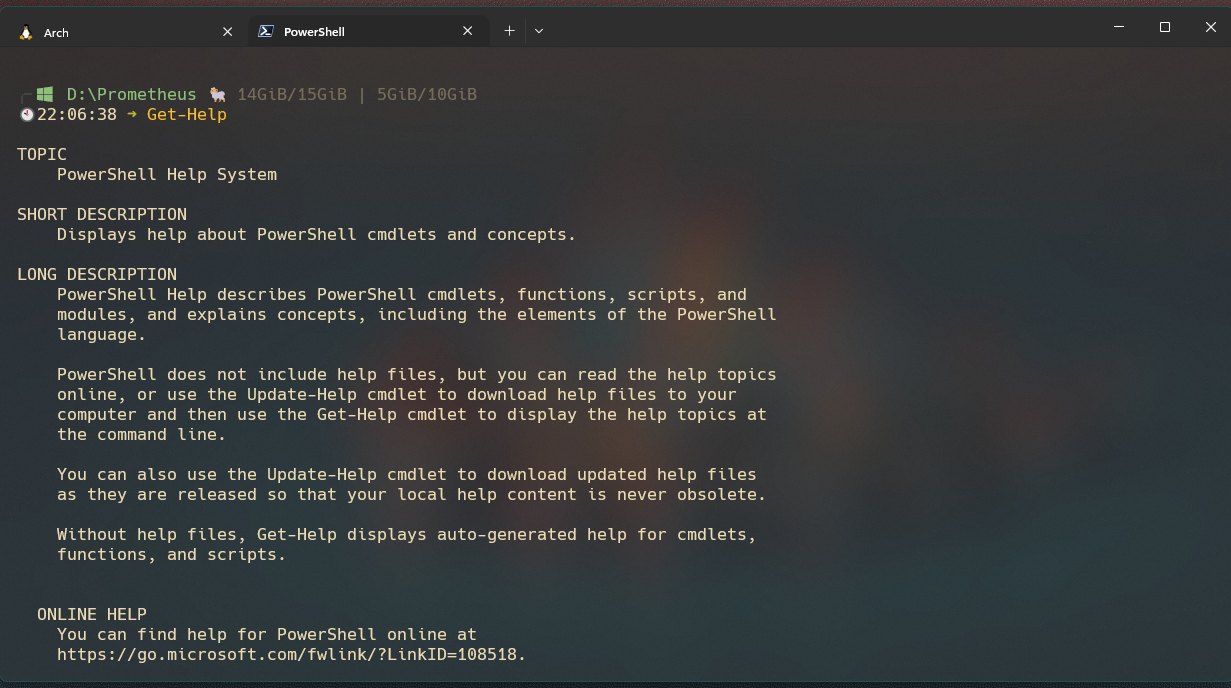
Get-Help
The Get-Help command is a crucial tool for anyone using PowerShell. It grants access to the information you need to run and work with all available commands. To use this command, simply type it in the PowerShell terminal.
Set-ExecutionPolicy
PowerShell restricts scripting by default to prevent malicious scripts from executing in the environment. To run your own scripts, you’ll need to enable scripting. The Set-ExecutionPolicy command allows you to control the level of security surrounding PowerShell scripts. You can set four security levels:
- Restricted: Default security level that blocks PowerShell scripts from running, allowing only interactive commands.
- All Signed: Permits scripts to run only if they are signed by a trustworthy publisher.
- Remote Signed: Allows locally-created scripts to run and remotely-created scripts if signed by a reputable publisher.
- Unrestricted: Permits all scripts to run by removing all restrictions from the execution policy.
To find out the current execution policy, use the Get-ExecutionPolicy command.
To read more about this command, you can use the Get-Help command or visit the Microsoft Documentation.
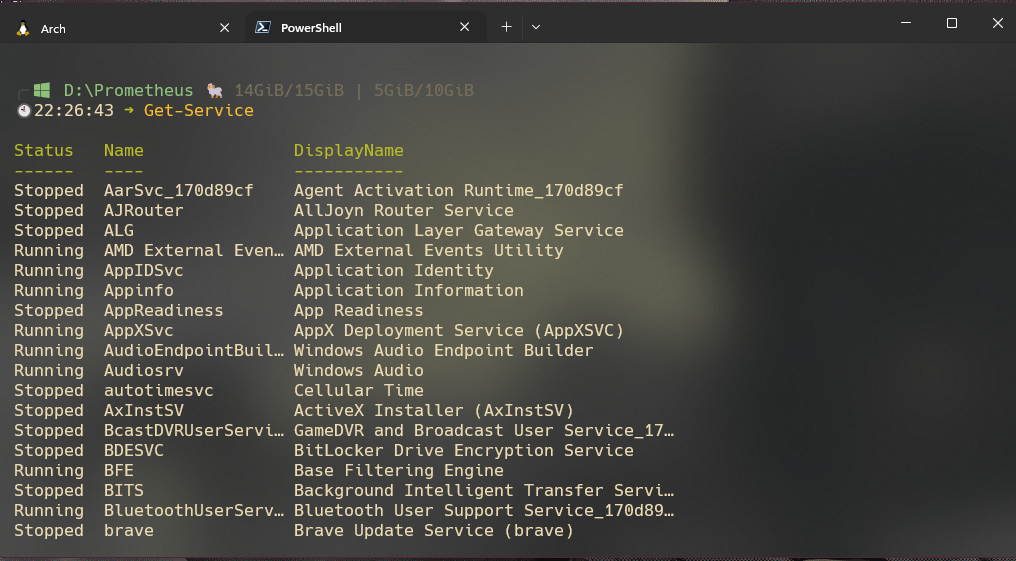
Get-Service
The Get-Service command retrieves information about the services installed on your computer. It allows you to find out the status of a service, start or stop a service, and even change the properties of a service. To use this command, type it in the PowerShell terminal.
Get-EventLog
Use PowerShell to parse your machine’s event logs with the Get-EventLog cmdlet. For example, to view the Application log, use the following command:
Get-EventLog -Log "Application"
You can also use various options with this command for verbose output, error handling, and more.
Get-Process
The Get-Process command allows you to get a quick list of all the currently running processes. You can also filter processes based on specific criteria. For example, to get all processes with a working set greater than 20 MB, use the following command:
Get-Process | Where-Object {$_.WorkingSet -gt 20000000}
Stop-Process
Stop-Process is used to terminate processes that are frozen or no longer responding. You can specify the process name or use wildcard characters to stop multiple processes simultaneously. For example:
Stop-Process -processname notepad
Get-ChildItem
The Get-ChildItem cmdlet retrieves items in one or more specified locations, including files, directories, and other objects. It is a versatile tool for file and directory management. For example:
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Test
Examples: Get child items from a file system directory
This example gets the child items from a file system directory. The filenames and subdirectory names are displayed. For empty locations, the command doesn’t return any output and returns to the PowerShell prompt.
The Get-ChildItem cmdlet uses the Path parameter to specify the directory C:\Test. Get-ChildItem displays the files and directories in the PowerShell console.
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Test
Directory: C:\Test
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
d----- 2/15/2019 08:29 Logs
-a---- 2/13/2019 08:55 26 anotherfile.txt
-a---- 2/12/2019 15:40 118014 Command.txt
-a---- 2/1/2019 08:43 183 CreateTestFile.ps1
-ar--- 2/12/2019 14:31 27 ReadOnlyFile.txt
By default Get-ChildItem lists the mode (Attributes), LastWriteTime, file size (Length), and the Name of the item. The letters in the Mode property can be interpreted as follows:
- l (link)
- d (directory)
- a (archive)
- r (read-only)
- h (hidden)
- s (system)
Combine Commands with Scripts
PowerShell’s true power lies in its ability to combine the simplicity of command-line commands with the flexibility of a full-fledged programming language. It empowers users to streamline their daily tasks, automate time-consuming processes, and unleash their creativity to build sophisticated solutions.
For instance, here are two custom scripts that demonstrate the power of PowerShell:
1. Sudo Script
The following script allows users to run a command or script with elevated privileges using Windows Terminal. It simplifies the process of running PowerShell commands with administrative privileges.
function sudo {
if ($args.Count -gt 0) {
$argList = "& '" + $args + "'"
$wtExe = "wt.exe"
Start-Process -FilePath $wtExe -ArgumentList "-p", "Windows PowerShell", "-NoExit", "-c", $argList -Verb RunAs
}
else {
$wtExe = "wt.exe"
Start-Process -FilePath $wtExe -ArgumentList "-p", "Windows PowerShell", "pwsh.exe" -Verb RunAs
}
}
2. Remove Item Script
This script is a user-defined PowerShell function that simplifies the process of removing files and folders. It enforces mandatory parameter usage, allows users to pass the path as the first argument without specifying the
parameter name, and ensures that a valid non-empty path is provided.
function rm {
[CmdletBinding()]
param (
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true, Position=0)]
[ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
[string]$Path
)
Remove-Item -Path $Path -Recurse -Force
}
PowerShell Project Ideas
The flexibility and power of PowerShell open up a wide range of project possibilities. Here are some ideas to get you started:
-
System Monitoring and Reporting: Develop a script that monitors system health and performance, generating reports on CPU usage, memory, disk space, and network connectivity.
-
Automated Backup and Restore: Create a script to automate the backup and restoration of important files and directories.
-
User Account Management: Build a script to automate user account creation, modification, and deletion tasks on Windows.
-
Software Deployment and Updates: Develop a script to automate the deployment and updating of software applications on multiple computers.
-
Log Analysis and Event Monitoring: Create a script that monitors event logs and generates alerts or reports based on specific events or patterns.
-
Network Configuration Management: Build a script to manage network devices and configurations, such as routers and switches.
-
Automated Testing: Use PowerShell to automate the testing of software applications by simulating user interactions.
-
Azure/AWS Cloud Automation: Automate cloud infrastructure provisioning and management on platforms like Microsoft Azure or Amazon Web Services (AWS).
-
Web Scraping and Data Retrieval: Create a script to scrape data from websites and APIs for analysis or integration with other systems.
-
Automated Email Notifications: Develop a script that monitors specific events and sends automated email notifications to specified recipients.
-
Scheduled Task Automation: Build a script to manage scheduled tasks on Windows, creating, modifying, and deleting tasks as needed.
With PowerShell, the possibilities are endless. It is a powerful tool that allows you to automate tasks, manage Windows systems efficiently, and unleash your creativity to build innovative solutions.
Conclusion:
PowerShell is a powerful and versatile tool that has become essential for IT professionals and system administrators. With its object-oriented approach, extensive cmdlets, and .NET integration, PowerShell offers an efficient way to manage Windows systems and automate tasks.
Throughout this blog post, we explored key PowerShell features, essential commands like Get-Command, Get-Help, Set-ExecutionPolicy, Get-Service, and Get-ChildItem, and how to combine commands with custom scripts.
PowerShell’s scripting capabilities enable automation of repetitive tasks, ensuring consistent configurations and reliable processes. Exciting project ideas, from system monitoring to cloud automation, demonstrate its endless possibilities.
With cross-platform compatibility, PowerShell continues to be a go-to solution for automation and administration, making it an invaluable tool in the IT world. Embrace PowerShell to streamline operations and elevate system management to new heights.
With that, we will see you next time.❤️❤️
Credit:
This article was written by Abdul Rafay and published on Future Insight.
Contact Us:
If you encounter any issues or have any questions regarding any of the articles on this website, please do not hesitate to contact the website’s support team. Your feedback is important and the team is dedicated to providing prompt and effective assistance to ensure a positive user experience.
To access the contact page, simply click on the “Contact” tab in the navigation menu or visit the following URL: contact page. From there, you can fill out a contact form or find additional information on how to get in touch with the support team.
Don’t let any questions or concerns go unanswered - reach out to the support team for help and guidance. They are committed to providing excellent customer service and will do everything possible to ensure that you have a seamless experience on the website.
Supporting Materials
Here are all of the links and references that I used to write this blog, so feel free to visit them to get some more help.
Knowledge Nexus
GitHub Repository:
Thumbnail