----
Linear regression is a powerful and widely-used statistical technique that can be used to model the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. It is commonly used in various fields, including economics, social sciences, engineering, and machine learning. Linear regression aims to find the best-fit line that describes the linear relationship between the independent and dependent variables, allowing for the prediction of the dependent variable for a given value of the independent variable. In this blog, we will explore the concept of linear regression, its types, and how to implement it using Python.
In this Blog post you will learn all the basic and advance level for Linear Regression with Examples as well. So get ready with me because it will be fun.
Linear Regression
So there are multiple ways you can define linear regression, but the simplest way to define it is that it is a supervised learning model in which this model will find the best linear line between two independent or dependent variables. This model will find the perfect relation between two or more than two variables. This entire work is known as a linear regression model.
Type:
Linear Regression is two type Simple and Multiple Linear Regression Model
Simple Linear Regression is where only on independent variable is present and the model will find the relation between independent variables.
Whereas in Multiple Linear Regression there will be more than one independent variable and the model have to find relation between them.
Mathematical Equation:
Simple Linear Regression
Equation of Simple Linear Regression, where bo is the intercept, b1 is coefficient or slope, x is the independent variable and y is the dependent variable.
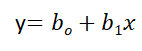
Multiple Linear Regression
Equation of Multiple Linear Regression, where bo is the intercept, b1,b2,b3,b4…,bn are coefficients or slopes of the independent variables x1,x2,x3,x4…,xn and y is the dependent variable.
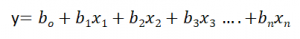
A Linear Regression model’s main aim is to find the best fit linear line and the optimal values of intercept and coefficients such that the error is minimized. Error is the difference between the actual value and Predicted value and the goal is to reduce this difference.
#Important Things to Train a Model: There are some important thing that are required to be done when you need to train any machine learning model and all of them are stated bellow;
- Load dataset.
- Clean Dataset.
- Visualize Dataset.
- Split the dataset into Training Set and Testing Set.
- Train the model using training Dataset.
- Use some king of learning rate and Fix the Mean Square Error
- Check the accuracy of the model.
- Test or Predict the model using testing Dataset.
- Visualize the new predication.
Implementation:
Here is a simple example of Linear regression that will help you to understand with code.
Linear Regression with Boston Data Set:
- Importing different libraries and the dataset called Boston
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn import metrics
%matplotlib inline
- Loading the Dataset & Printing the dataset:
data= load_boston()
In the above code we are using the data-frame library and CSV library using the csv library we are reading the excel sheet that will contain all of the data, using data frame we are loading the data into a Visualize form.
data
- Getting the Data & feature name:
# The explanatory variables.
X = data['data']
header = data['feature_names']
- Reshaping:
Y = data['target']
Y = Y.reshape(-1,1)
- Data into Data Frame:
df = pd.DataFrame(np.append(X,Y,axis = 1))
df.columns = list(header)+['PRICE']
- Rounding the Data Set:
np.round(df.corr(),2)
- Apply Linear Regression Model: So when you want to use linear regression, there are two ways: 1 You can use the built-in model and library; this method is fast and does not require much logic. 2. You can code linear regression from scratch; by doing this, you can control the logic of the application and push the model to its limits.
In this Blog I will be using built in functions and libraries to compute Linear Regression.
lm = LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True)
- Fitting the Data into Model:
lm.fit(df[['parent']],df[['child']])
- Display the results in the form of Data frame:
# Display the parameters as a DataFrame.
parametersDF = pd.DataFrame(lm.coef_,index=['Parameter Value'],columns=header)
parametersDF['Intercept'] = lm.intercept_[0]
parametersDF
In the above patch of code, we are reading the training data set into a data frame, and then that data frame will be displayed.
- Predicting the Values: Now our data is fit and model is trained, we will start with the predication.
predicty=lm.predict(df[['parent']])
- Result: Now we will start with the displaying the result.
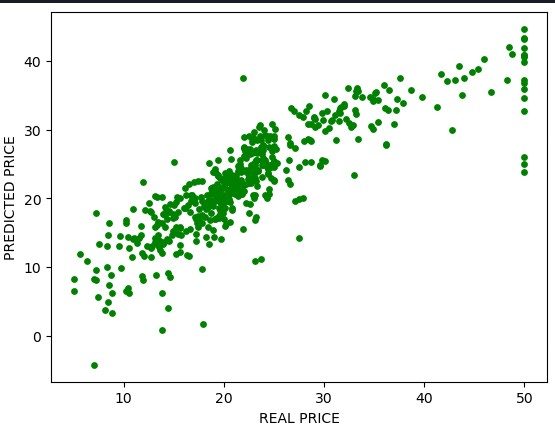
# Display real Y vs predicted Y.
plt.scatter(Y,predicty,c = 'green', s=15, alpha=1)
plt.xlabel('REAL PRICE')
plt.ylabel('PREDICTED PRICE')
plt.show()
Once the code is compiled then your output should like this:
Conclusion:
Linear regression is great. It has its ups and downs, but over all, it can be used for a lot of things. So learn it and use it. I am still learning and making sure that my work is good and flawless.
Contact Me:
If you have any questions, please contact me
I will see you next time❤️.
Credit:
This article was written by Abdul Rafay and published on Future Insight.
Contact Us:
If you have any questions, please contact
Future Insight:
Author:
Abdul Rafay:
Supporting Materials
Here are all of the links and references that I used to write this blog, so feel free to visit them to get some more help.
Knowledge Nexus
GitHub Repository
Thumbnail:
